Here I am going to write on simple basic module which can load into kernel and can remove from kernel . This sample module do nothing we can see the module loading and removing message in syslog.
First the useful things to write code
First the useful things to write code
- Your favorite code editor
- Here I used geany code editor
- Header files
- basic header file/libraries you must include in c file are
- linux/init.h
- linux/module.h
- Basic functions
- basic functions/macros to add your function to kernal ar
- module_init(fun);
- module_exit(fun);
- Makefile
- some commands to view the log
#include <linux\init.h>
#include <linux\module.h>
int ex1_simple_module_init(void)
{
printk(KERN_ALERT"Module ex1 Inside the Function %s",__FUNCTION__);
return 0;
}
void ex1_simple_module_exit(void)
{
printk(KERN_ALERT"Module ex1 Inside the Function %s",__FUNCTION__);
}
module_init(ex1_simple_module_init);
module_exit(ex1_simple_module_exit);
the above c code havin 2 user function
ex1_simple_module_init() and ex1_simple_module_exit()
and both having printk functions . the printk function send the data to system log . we can see that data in "var/log/syslog" file
module_init() function take the function as argument and sends that function to kernel as init funtion and module_exit() function send the function to kernel as exit function
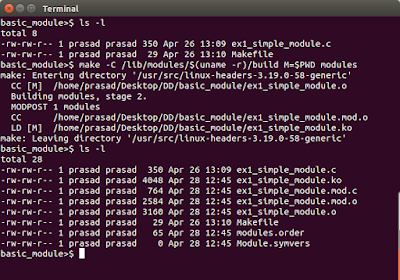
to compile the kernel we need to know the current kernel version . To get that we can use the command
uname -r
Now write the make file to compile the module
Create a file with name Makefile and insert the below code in that
obj - m := ex1_simple_module.o
here the file name is ex1_simple_module.c so we use ex1_simple_module.o as output .This simple line in the makefile compile our c code and generate object file.
To run the Makefile we need to use the below command in bas terminal
make -C /lib/modules/$(uname -r)/build M=$PWD modules
here the kernel version is got from uname -r command and the source file directory is fetch from PWD command. So we must run this command from the directory where the source file is stored
now the source is compiled and the .ko files are generated now we can insert and remove the module to kernel.To do this first we need to follow the syslog. For that we can us the below command in terminal.
sudo tail -f /var/log/syslog
here tail means print the tail part(last lines)
-f means follow the last lines in the file syslog
after this command current terminal will the print syslog data so we need to open the other terminal to insert the module into kernel
To insert the module use insmod command and to remove use rmmod command
sudo insmod ./ex1_simple_module.ko sudo rmmod ex1_simple_module
That it . I hope this post is useful to you .Please comment below and check out other posts and my youtube channel